The Ultimate Guide to Understanding VLANs
Virtual LANs (VLANs) have become a foundational technology in modern networking, offering significant benefits in terms of security, efficiency, and network management. If you’re in the tech industry, whether you’re an IT manager, network engineer, or cybersecurity analyst, understanding VLANs is essential. This comprehensive guide will delve into everything you need to know about VLANs, from what they are to how they work, their benefits, and best practices for implementation.
What is a VLAN?
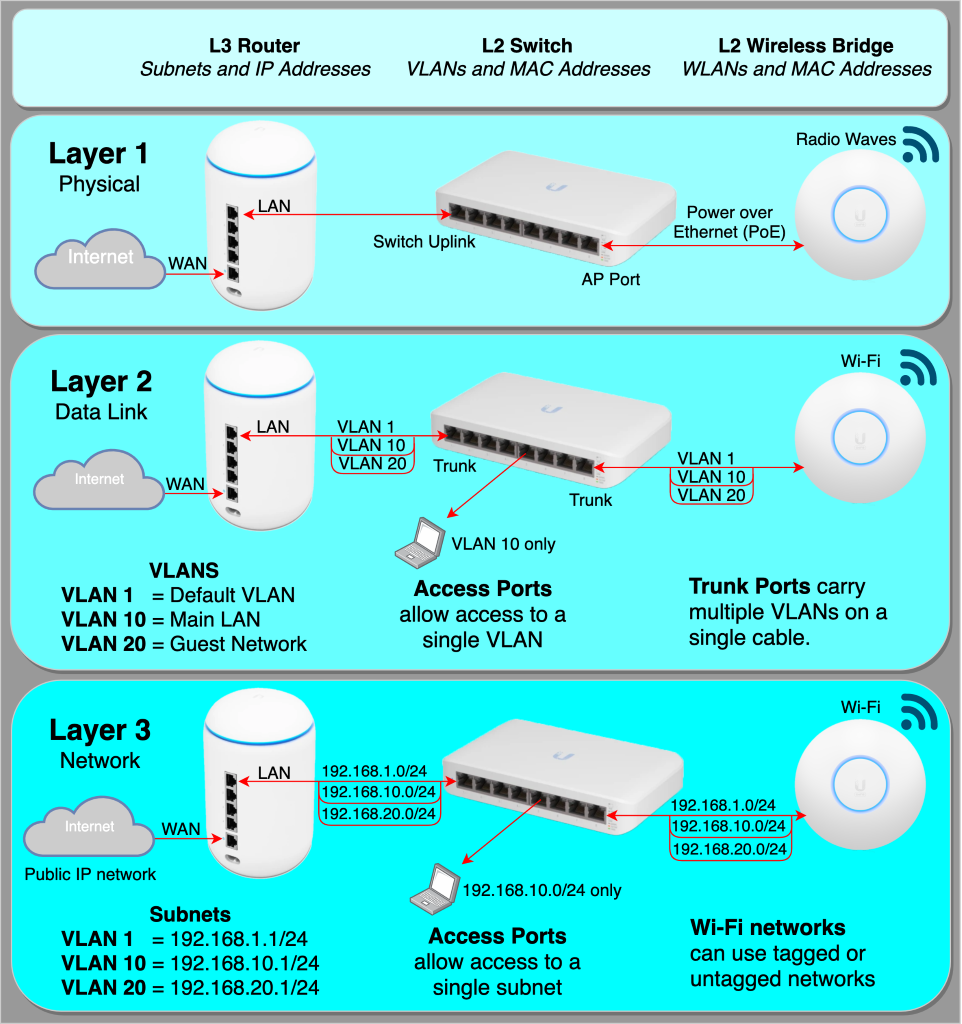
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a method used in networking to create distinct broadcast domains within a single physical network. In simpler terms, a VLAN allows network administrators to segment a larger network into smaller, isolated subnetworks, each of which can act as if it’s a separate physical network. This segmentation is done at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model using a technique called VLAN tagging.
How VLANs Work
VLANs operate by tagging each packet of data with a VLAN ID. This ID specifies which VLAN the packet belongs to, ensuring that devices within the same VLAN can communicate with each other directly while isolating traffic from other VLANs. Here’s a breakdown of the key components and processes involved:
- VLAN Tagging: When data packets are sent across the network, they are tagged with a VLAN ID. This tagging is done using a protocol like IEEE 802.1Q, which inserts a tag into the Ethernet frame. This tag contains the VLAN ID, allowing network switches to know which VLAN the packet belongs to.
- Switches and VLANs: Managed switches are central to VLAN operation. These switches can recognize VLAN tags and route traffic accordingly. For example, if two computers are in different VLANs but connected to the same switch, the switch will ensure that the traffic does not cross between the two VLANs unless explicitly allowed.
- Inter-VLAN Routing: While VLANs isolate traffic, there are scenarios where communication between VLANs is necessary. This is achieved through inter-VLAN routing, usually handled by a Layer 3 switch or a router. This device routes traffic between VLANs while maintaining the isolation of VLAN-specific traffic.
- VLAN Trunking: VLAN trunking allows VLANs to be extended across multiple switches. A trunk link carries traffic for multiple VLANs between switches, ensuring that VLAN segmentation is maintained across the network.
Benefits of VLANs
Implementing VLANs in your network architecture offers several advantages:
- Improved Security: VLANs help segregate sensitive data and reduce the risk of unauthorized access. For example, you can place the finance department on a separate VLAN from the rest of the company, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
- Better Network Performance: By segmenting a network, VLANs reduce the size of broadcast domains. This minimizes unnecessary traffic, leading to more efficient network performance and reducing the chances of broadcast storms.
- Simplified Network Management: VLANs allow for easier management of large networks. You can organize devices based on their function or department, making it easier to apply policies, manage traffic, and troubleshoot issues.
- Flexibility and Scalability: VLANs provide the flexibility to reconfigure the network without altering physical cabling. This is particularly useful in dynamic environments where network requirements frequently change.
Types of VLANs
VLANs can be categorized based on their use cases:
- Default VLAN: All ports on a switch are part of the default VLAN until they are reassigned. Typically, this is VLAN 1.
- Data VLAN: Also known as user VLANs, these are the most common types and are used to carry user-generated traffic, such as email and web browsing.
- Voice VLAN: Designed specifically for VoIP traffic, voice VLANs prioritize voice data to ensure call quality.
- Management VLAN: This VLAN is used for managing the network devices. It is critical for ensuring secure access to the configuration interfaces of switches and routers.
- Native VLAN: Used in VLAN trunking, the native VLAN carries untagged traffic. It’s crucial to secure the native VLAN to prevent VLAN hopping attacks.
Best Practices for VLAN Implementation
To get the most out of VLANs and ensure a secure and efficient network, follow these best practices:
- Plan Your VLAN Architecture: Before implementation, map out the VLAN structure. Consider the different departments or services that require segregation and how they will interact.
- Use Consistent VLAN Numbering: Maintain a consistent VLAN numbering scheme across your network. This helps in troubleshooting and managing VLANs more effectively.
- Secure the Native VLAN: By default, VLAN 1 is often used as the native VLAN, but it is recommended to change this to another VLAN and secure it to prevent VLAN hopping attacks.
- Implement Inter-VLAN Routing with Caution: Only allow inter-VLAN routing when necessary, and ensure that firewalls or access control lists (ACLs) are in place to regulate the traffic between VLANs.
- Regularly Audit VLAN Configurations: Periodically review and audit your VLAN setup to ensure that it meets your organization’s security and operational needs.
- Training and Documentation: Ensure that your IT staff is well-trained on VLAN configurations and that all setups are thoroughly documented.
Common VLAN Issues and Troubleshooting
Despite their benefits, VLANs can introduce complexity into a network. Here are some common issues and how to troubleshoot them:
- VLAN Mismatch: If VLAN IDs are not consistent across switches, it can lead to communication issues. Regularly verify VLAN configurations on all switches.
- Native VLAN Misconfiguration: Misconfiguring the native VLAN can lead to security vulnerabilities. Ensure that the native VLAN is correctly set and secured on all trunk links.
- Inter-VLAN Routing Problems: Ensure that routing devices have the correct routing protocols enabled and that ACLs are not inadvertently blocking necessary traffic.
Conclusion
VLANs are a powerful tool in modern networking, offering security, efficiency, and ease of management. Whether you’re setting up a small office network or managing a large enterprise environment, understanding and properly implementing VLANs can significantly enhance your network’s performance and security. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can create a robust and scalable network that meets your organization’s needs.
If you’re ready to take your network management to the next level, consider consulting with an IT professional to optimize your VLAN setup and ensure your network is secure and efficient.

